Nature's Tiny Terrorist: The Screwworm's Cross-Border Battle and its Economic Aftershocks
Explore the New World Screwworm: a tiny pest with massive economic & geopolitical impact. Uncover the US-Mexico border crisis, innovative defenses & the silent war for food security.
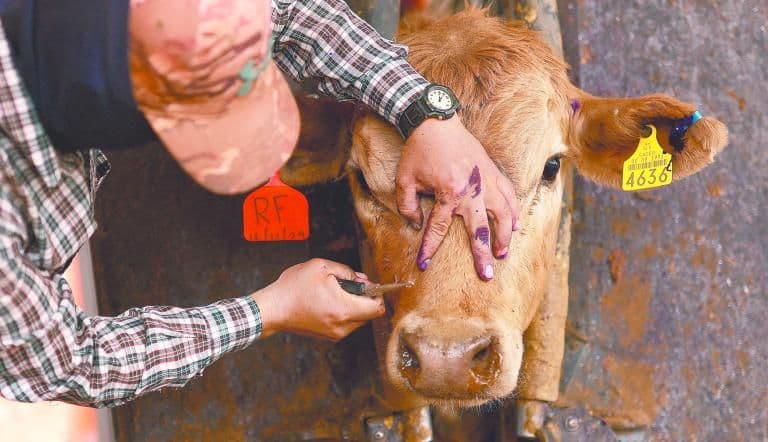

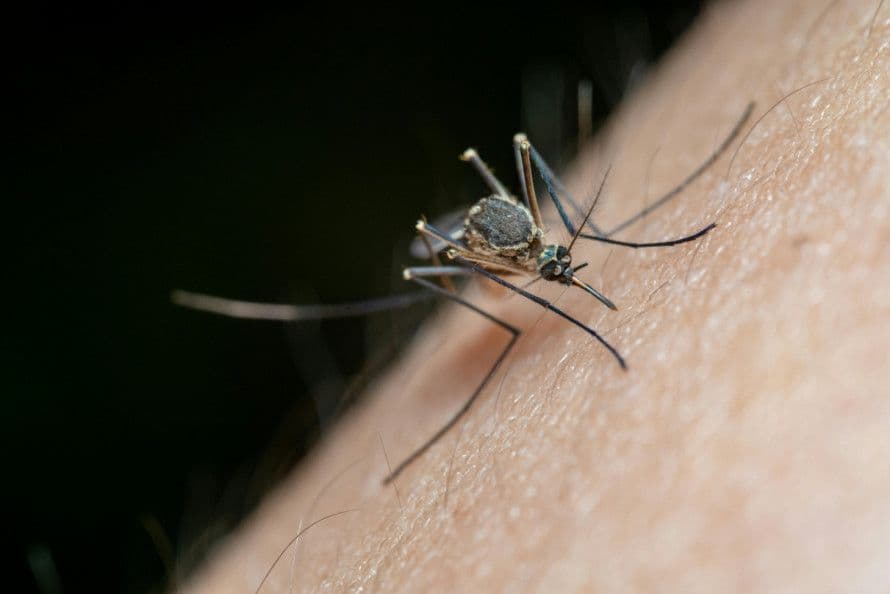
Unmasking the Flesh-Eating Foe: What is the New World Screwworm?
Imagine a silent predator, not a beast of the wild, but a microscopic menace whose very existence threatens entire economies. That's the , or Cochliomyia hominivorax, a parasitic insect that's anything but a simple worm. It's actually the larva of a fly, notorious for its gruesome feeding habits. These insidious larvae target warm-blooded animals, from domestic livestock like cattle to various wild mammals, and even, on occasion, humans. The female fly lays her eggs in any open wound or body cavity; once hatched, the larvae burrow deep into the flesh, consuming living tissue with a horrifying efficiency. This leads to severe lesions, secondary infections, significant weight loss, a drastic drop in productivity, and ultimately, if left untreated, the death of the host. The recent confirmation of a case in , , serves as a stark reminder of why controlling this pest is a top priority for agricultural and livestock health, posing a direct threat to rural economies and food security.
A Line in the Sand: The Escalating Bi-National Border Crisis
The discovery of the in wasn't just a biological alarm; it immediately ignited a high-stakes geopolitical crisis along the . Situated less than 113 kilometers from American soil, this outbreak transformed a local problem into an international emergency, triggering immediate and severe restrictions on the movement of Mexican livestock. This isn't merely about animal health; it’s about a direct challenge to binational agro-trade, with the explicitly demanding adhere to a Joint Action Plan. The response has been unequivocal and assertive, closing its borders to imported cattle, bison, and horses from —a third such closure in less than a year. With statements like "protecting the from the screwworm is non-negotiable" and warnings of "decisive action... even in absence of cooperation," the has drawn a clear line, signaling a readiness to safeguard its livestock industry without relying on collaboration. This firm stance underscores the profound diplomatic tensions simmering beneath the surface of this biological threat.
Strategic Defense: Science and Surveillance on the Front Lines
In the face of this escalating crisis, both nations have mobilized significant resources, albeit with varying degrees of perceived cooperation, to deploy strategic defenses. The , since June 2025, has committed nearly $100 million to an ambitious plan, investing in innovative technology for eradication, developing facilities for the mass dispersal of sterile flies—a cornerstone of the —and intensifying border surveillance. This includes installing some 8,000 traps across , , and , processing over 13,000 samples without detecting the pest on territory so far. Meanwhile, has implemented a digital dashboard for real-time case tracking, enhancing operational planning and technical cooperation within its borders. While these scientific and surveillance efforts represent a formidable shield against the screwworm's advance, the 's explicit warning that it will protect its territory "even if does not fully cooperate" highlights the complex dance between scientific collaboration and national sovereignty in this cross-border battle.

The Invisible Hand: Economic Fallout and Future Resilience
The screwworm's presence, though tiny, wields an invisible hand capable of crippling economies. The recent outbreak in , particularly its proximity to the —a vital commercial artery for trade—has cast a long shadow over producers. The immediate restrictions on livestock movement and the recurrent border closures by the , now the third time in less than a year, directly translate into significant financial losses for exporters. Beyond trade, the insidious nature of the pest itself inflicts substantial economic damage: reduced animal productivity, costly treatments, and potential mortality rates that can decimate herds. The views this as its "most direct threat" to date, emphasizing the immense economic stakes involved. This crisis serves as a stark reminder that biosecurity failures have far-reaching economic ramifications, necessitating not only robust scientific responses but also the development of resilient, cooperative frameworks to ensure the stability of the binational agricultural sector and protect the livelihoods it sustains.
Related Articles

The Unintended Consequence: Unmasking the Paradox Behind Ukraine's Locust Surge

The Unintended Consequence: Unmasking the Paradox Behind Ukraine's Locust Surge

Whispers on the Wind: Ukraine's Locust Surge and the Unforeseen Harvest of Conflict

Whispers on the Wind: Ukraine's Locust Surge and the Unforeseen Harvest of Conflict

France's Lumpy Skin Shock: The High Stakes and Hard Choices in a Nationwide Eradication Effort

France's Lumpy Skin Shock: The High Stakes and Hard Choices in a Nationwide Eradication Effort
The Silent Scourge: Unmasking Ukraine's Evolving Midge Menace
